MIL-DTL-5515F
4.6.4.1 Output pressure. Connect pump to the fluid supply and a pressure regulator that is regulated to the required
output pressure as specified on figure 2. Operate pump to provide flow at this regulated pressure.
MIL-PRF-5506
or MIL-PRF-
83282 or MIL-
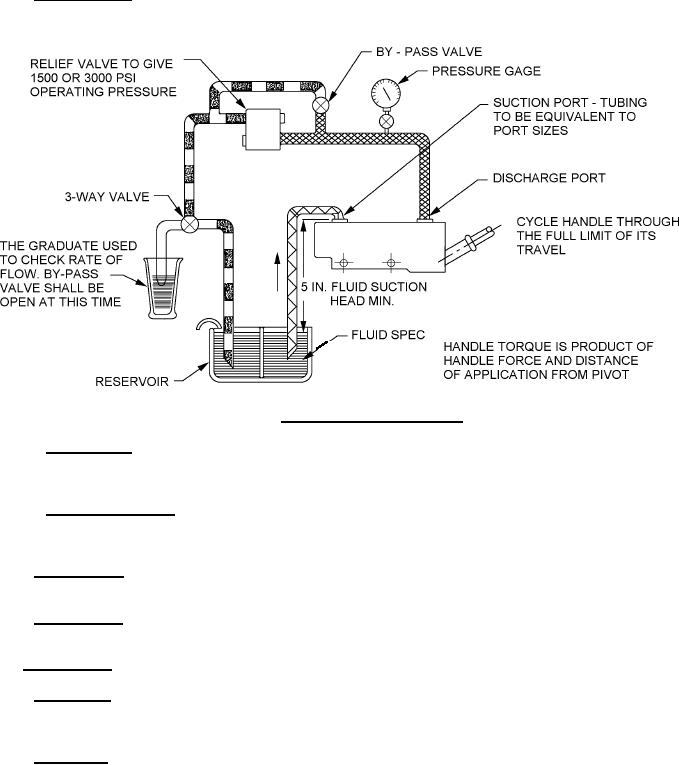
FIGURE 2. Hand pump cycling test set-up.
4.6.4.1.1 Handle torque. After operating the pump to produce the required output pressure (see 4.6.5.1), increase
flow by slowly applying loads at not greater than 30 inches from pivot point of a suitable handle to determine the
necessary torque for the entire stroke in both directions.
4.6.4.1.2 Mechanical efficiency. Using loads determined in handle torque tests (see 4.6.4.1.1), and the mechanical
advantage provided by the geometry of the linkages, determine the maximum axial input loads on the pump piston for
both stroke directions. Calculate mechanical efficiency for both stroke directions.
4.6.4.2 Proof pressure. Apply a load, sufficient to produce the required proof pressure, at the end of a suitable
handle for 5 minutes for each stroke direction.
4.6.4.3 Burst pressure. Apply required burst pressure with an external hydraulic power supply to all internal cavities
of the pump that are subjected to operating pressure.
4.6.5 Cold operation.
4.6.5.1 Cold priming. Cold soak an empty pump and test equipment as specified on figure 1 at not less than
-65°F (-54°C) for not less than 72 hours. Test pump in accordance with priming testing (see 4.6.2), except at the cold
soak temperature.
4.6.5.2 Cold cycling. Connect the above cold-soaked pump to a pressure regulator that is regulated to the required
output pressure. The suction line may be changed to provide not less than 5 inches for the suction head. Operate
the pump at not less than 20 cycles per minute through at least 25 complete cycles with the pump and fluid held at
-55°F (-48°C) to -65°F (-54°C) to:
a. Produce flow at required output pressure
b. Determine output volume per cycle (see 3.6.7.1).
Cycle the pump at sufficient intervals to determine binding or other malfunctions due to differential expansion of
mating parts during rapid warm-up to 120°F - 129°F (49°C - 54°C).
7
For Parts Inquires call Parts Hangar, Inc (727) 493-0744
© Copyright 2015 Integrated Publishing, Inc.
A Service Disabled Veteran Owned Small Business